Unlocking Innovation with Genomics & Bioinformatics APIs
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving world of life sciences, Genomics & Bioinformatics APIs are becoming the backbone of modern research and innovation. These interfaces allow researchers, developers, and organizations to access complex genomic datasets, perform advanced analyses, and integrate cutting-edge bioinformatics tools into their workflows without building everything from scratch. By bridging the gap between raw biological data and actionable insights, APIs are transforming how we understand genetics, disease pathways, and personalized medicine.
Why Genomics & Bioinformatics APIs Matter
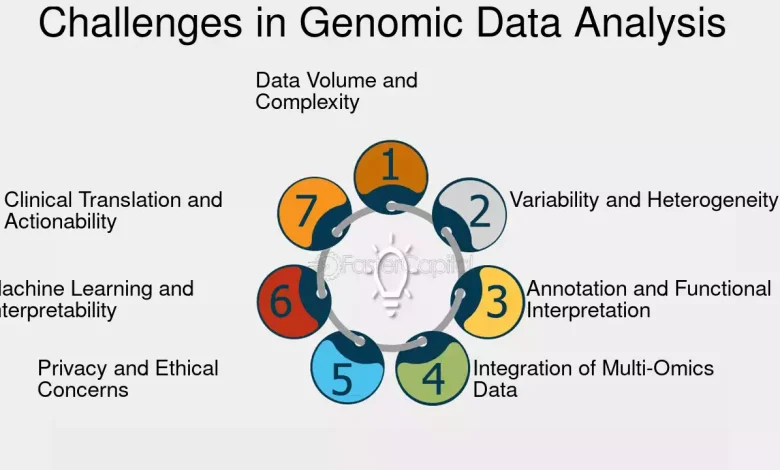
The explosion of genomic data—from whole-genome sequencing to RNA analysis—has created both unprecedented opportunities and enormous computational challenges. Manually analyzing such massive datasets is not only time-consuming but also prone to errors. That’s where Genomics & Bioinformatics APIs come in:
- Simplified Access – APIs provide standardized, programmatic access to genomic databases, enabling researchers to pull data from multiple sources efficiently.
- Interoperability – They allow different bioinformatics tools and platforms to work together seamlessly, making pipelines more robust and reproducible.
- Scalability – Whether you’re analyzing a single genome or thousands, APIs allow operations to scale without needing enormous in-house infrastructure.
- Innovation Acceleration – With APIs, startups and established labs can rapidly prototype new tools, apps, and diagnostic platforms without reinventing the wheel.
Core Features of Genomics & Bioinformatics APIs
Modern APIs in genomics and bioinformatics are designed to tackle the unique challenges of the field. Some of the key capabilities include:
- Data Retrieval – Access sequences, variants, annotations, and expression datasets from repositories like NCBI, Ensembl, or UCSC Genome Browser.
- Analysis Pipelines – Run workflows such as variant calling, gene expression profiling, or pathway enrichment directly through API endpoints.
- Visualization Tools – Generate graphs, heatmaps, or genomic plots programmatically to integrate into web apps or dashboards.
- Machine Learning Integration – Feed genomic data into predictive models for drug discovery, disease prognosis, or personalized treatment recommendations.
Use Cases Driving the Industry
The adoption of Genomics & Bioinformatics APIs is accelerating across multiple sectors:
- Healthcare & Precision Medicine – APIs enable hospitals and research centers to integrate patient genomic data with clinical records, supporting personalized therapies.
- Pharmaceutical Research – Drug discovery pipelines benefit from APIs that analyze genetic markers, protein interactions, and population genetics efficiently.
- Agrigenomics – Agricultural research leverages APIs to analyze plant and animal genomes for traits like disease resistance or yield improvement.
- Academic Research – Universities and institutes can quickly access high-quality datasets for studies without maintaining extensive local databases.
Advantages Over Traditional Methods
Historically, bioinformatics analyses required significant computational expertise and local resources. APIs disrupt this model by offering:
- Ease of Integration – Developers can incorporate genomic tools into applications with minimal coding.
- Real-Time Updates – API-driven workflows always pull the latest data, reducing outdated information errors.
- Cost Efficiency – Cloud-based API services reduce the need for large computational infrastructure in-house.
- Collaboration & Reproducibility – Standardized API endpoints ensure analyses can be replicated and shared across teams globally.
Best Practices for Implementing Genomics & Bioinformatics APIs
To maximize benefits, organizations should consider the following strategies:
- Select APIs with Strong Documentation – Comprehensive guides, tutorials, and example queries reduce integration time and errors.
- Ensure Compliance – Many APIs deal with sensitive genomic or patient data, so compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, or other local regulations is critical.
- Optimize Data Handling – Use caching, batch processing, and asynchronous calls to manage large datasets efficiently.
- Monitor Performance & Errors – Set up logging and monitoring to detect failures, latency issues, or inconsistent data retrieval.
Future Trends
The future of Genomics & Bioinformatics APIs looks exciting and transformative:
- AI-Powered Insights – APIs will increasingly integrate machine learning to automate variant interpretation, disease prediction, and pathway analysis.
- Multi-Omics Integration – APIs will combine genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics data for holistic biological insights.
- Decentralized Data Access – Blockchain and secure federated APIs may allow researchers to share data safely across institutions without compromising privacy.
- Personalized Applications – Consumer-facing health and wellness apps may tap APIs to provide genome-informed lifestyle and nutrition recommendations.
Conclusion
Genomics & Bioinformatics APIs are no longer optional—they are essential tools for anyone working at the intersection of biology and technology. They empower researchers, clinicians, and developers to unlock insights from vast genomic datasets, improve reproducibility, and accelerate innovation. By providing seamless access to complex bioinformatics resources, these APIs are driving a future where personalized medicine, advanced drug discovery, and global collaborative research are not just possible but practical.
Harnessing the potential of these APIs today sets the stage for a smarter, faster, and more connected future in genomics research.



